Wayfair is a furniture and household item eCommerce company founded in 2002 by Niraj Shah and Steve Conine. Wayfair initially operated as a simple drop shipping business but has since diversified its revenue generation strategy, and it makes money via product sales, installation services, advertising, and interchange fees.
| Business Model Element | Analysis | Implications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Wayfair’s value proposition revolves around offering a vast selection of home furnishings and décor, competitive prices, and a convenient shopping experience. For Customers, Wayfair provides: – Extensive Product Catalog: A wide range of furniture and home goods. – Competitive Pricing: Competitive prices and discounts. – Convenience: Easy online shopping with delivery options. For Suppliers, Wayfair offers: – Market Access: Access to a large customer base. – Sales Channel: An additional sales channel for suppliers. – Analytics: Data and insights to optimize product listings. Wayfair aims to simplify home shopping and offer a one-stop destination for all home furnishing needs. | Provides a comprehensive selection of home furnishings and décor products. Offers competitive prices and discounts to attract budget-conscious shoppers. Prioritizes convenience through online shopping and multiple delivery options. Grants suppliers access to a vast customer base and additional sales opportunities. Equips suppliers with data and insights to optimize their listings. Attracts customers seeking diverse home furnishing options and suppliers looking to expand their reach. Simplifies the home shopping process. | – Extensive product catalog caters to various home styles. – Competitive pricing attracts budget-conscious shoppers. – Convenience enhances the online shopping experience. – Market access benefits suppliers seeking growth. – Data and insights aid suppliers in optimizing their listings. – Simplifies home furnishing shopping. |
| Customer Segments | Wayfair serves multiple customer segments, including: 1. Individual Shoppers: Consumers looking for home furnishings and décor. 2. Interior Designers: Professionals seeking products for client projects. 3. Businesses: Businesses in need of office and commercial furnishings. Wayfair caters to diverse consumer and business needs in the home furnishing market. | Focuses on diverse customer segments within the home furnishing industry. Customizes user experiences based on individual preferences and needs. Provides a platform for various customer types, including individual shoppers, interior designers, and businesses. Offers a versatile range of products to meet varying demands. | – Serving diverse customer segments broadens the user base. – Customized experiences cater to individual preferences. – Provides a platform for various customer types. – Offers a versatile product range to meet diverse needs. |
| Distribution Strategy | Wayfair’s distribution strategy relies on its e-commerce platform and partnerships with various suppliers. Customers can browse and purchase products through Wayfair’s website and mobile app. Wayfair also collaborates with suppliers to expand its product catalog and improve delivery options, including dropshipping. The company’s supply chain and logistics operations ensure timely deliveries. | Utilizes its e-commerce platform, including the website and mobile app, to provide easy access for customers. Collaborates with suppliers to continuously expand the product catalog and offer a wide selection. Partners with suppliers for efficient dropshipping and improved delivery options. Maintains robust supply chain and logistics operations to ensure timely product deliveries to customers. | – E-commerce platform accessibility aligns with user preferences. – Partnerships with suppliers expand the product catalog. – Dropshipping enhances delivery options. – Strong supply chain and logistics ensure timely deliveries. |
| Revenue Streams | Wayfair generates revenue primarily through the sale of home furnishings and décor products. Its revenue streams include: 1. Product Sales: Revenue generated from selling furniture and home goods. 2. Advertising and Commissions: Advertising fees and commissions from suppliers. 3. Delivery and Installation Services: Fees for delivery, assembly, and installation services. Product sales are the primary source of revenue. | Relies on product sales as the primary source of income, generating revenue from selling furniture and home goods. Earns additional income through advertising fees and commissions from suppliers. Provides delivery, assembly, and installation services for additional revenue. Prioritizes product sales to sustain operations and maintain competitive pricing. Offers supplementary services to enhance customer experience and increase revenue. | – Product sales provide a consistent revenue source. – Advertising and commissions add to income opportunities. – Supplementary services enhance customer experience and revenue. – Prioritizes product sales to maintain competitive pricing. |
| Marketing Strategy | Wayfair’s marketing strategy focuses on digital advertising, content marketing, and data-driven personalized recommendations. The company utilizes online advertising channels, including social media, search engines, and display ads, to reach a wide audience. Content marketing includes blog articles and guides to assist customers in their home furnishing decisions. Wayfair employs data analytics to provide personalized product recommendations and offers. | Emphasizes digital advertising to reach a broad online audience through channels like social media and search engines. Creates informative blog articles and guides to assist customers in their home furnishing decisions. Utilizes data analytics to offer personalized product recommendations and deals to customers, enhancing the shopping experience. Provides a seamless online shopping journey from product discovery to purchase. | – Digital advertising reaches a wide online audience. – Content marketing assists customers in their decisions. – Data-driven recommendations enhance the shopping experience. – Provides a seamless online shopping journey. |
| Organization Structure | Wayfair’s organizational structure includes teams dedicated to software development, supplier relationships, marketing, logistics, customer support, and data analytics. Software development teams focus on platform enhancements. Supplier relationship teams collaborate with suppliers to expand the product catalog. Marketing teams handle promotional efforts. Logistics teams ensure efficient supply chain operations. Customer support teams assist users with inquiries. Data analytics teams provide insights for personalized recommendations. This structure supports platform excellence, supplier relationships, user satisfaction, and data-driven strategies. | Employs specialized teams for software development, supplier relationships, marketing, logistics, customer support, and data analytics. Prioritizes platform enhancements through development teams. Collaborates with suppliers to expand the product catalog and enhance relationships. Manages promotional efforts through marketing teams. Ensures efficient supply chain operations through logistics teams. Assists users with inquiries through customer support teams. Leverages data analytics for data-driven strategies and personalized recommendations. | – Specialized teams drive platform enhancements. – Collaborates with suppliers for product expansion and relationships. – Manages promotional efforts effectively. – Ensures efficient supply chain operations. – Assists users with inquiries for enhanced satisfaction. – Leverages data analytics for personalized recommendations. |
| Competitive Advantage | Wayfair’s competitive advantage stems from its vast product catalog, competitive pricing, user-friendly e-commerce platform, supplier partnerships, and data-driven personalization. Vast Product Catalog: Offers a wide selection of home furnishings. Competitive Pricing: Provides competitive prices and discounts. User-Friendly Platform: Offers an intuitive and convenient online shopping experience. Supplier Partnerships: Collaborates with suppliers to expand the catalog. Data-Driven Personalization: Offers personalized product recommendations. Wayfair distinguishes itself as a one-stop destination for home furnishings. | Derives a competitive advantage from: – A vast product catalog with diverse options. – Competitive pricing and discounts for budget-conscious shoppers. – An intuitive and convenient e-commerce platform. – Collaborative supplier partnerships for catalog expansion. – Data-driven personalization for enhanced user experiences. Stands out as a comprehensive home furnishing platform with an extensive selection and personalized recommendations. | – Diverse product catalog caters to various home styles. – Competitive pricing attracts budget-conscious shoppers. – User-friendly platform enhances the online shopping experience. – Collaborative supplier partnerships expand the catalog. – Data-driven personalization adds value to the user journey. – Stands out as a one-stop destination for home furnishings. |
History of Wayfair
Wayfair is a furniture and household item eCommerce company founded in 2002 by Niraj Shah and Steve Conine.
During the early 2000s, the long-time friends and co-founders noted that shopping for furniture and housewares lacked variety.
Consumers would be lucky to see three or four variations of the same product on a shelf in a store.
Businesses were also hamstrung because many did not have the physical floor space to showcase a diverse variety of options.
Inspired by Conine’s mother – who owned two furniture stores – the pair sought to move furniture shopping online and give consumers more choice in the process.
Racksandstands.com was launched in August 2002, an early eCommerce site selling storage furniture and media stands. The site became very popular, thanks in part to a diverse product range and good SEO.
To increase the legitimacy of their venture, Conine and Shah created holding company CSN Stores. Eventually, CSN Stores would encapsulate more than 200 different websites selling everything from bar stools to aviaries.
Expansion into the Canadian, British, and German markets soon followed as the company built a logistics network specially designed to ship large items quickly.
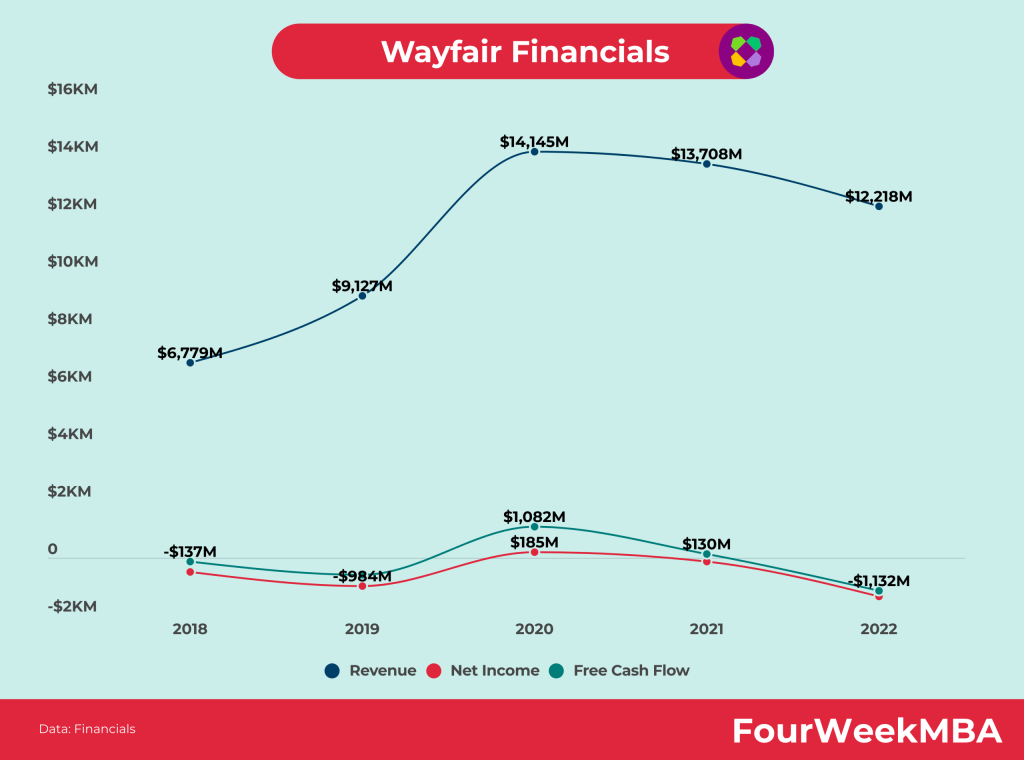
In 2011, the CSN Stores group of sites was consolidated and rebranded as Wayfair, Inc. Total net revenue for Wayfair was $3.7 billion in 2020, representing a 44.9% year-over-year increase.
Value Proposition
- Wide Product Selection: Wayfair offers a vast selection of furniture, home goods, decor, appliances, lighting, and outdoor products from thousands of brands and suppliers, providing customers with a comprehensive range of options to suit their individual style, budget, and needs.
- Competitive Prices: Wayfair provides competitive prices and value-oriented deals on its products, leveraging its scale, supplier relationships, and operational efficiency to offer affordable pricing and discounts to customers, ensuring cost-effective shopping and value for money.
- Convenience and Accessibility: Wayfair offers a convenient and accessible shopping experience through its user-friendly website and mobile app, allowing customers to browse, search, and purchase products anytime, anywhere, with easy navigation, intuitive filters, and secure payment options.
- Inspiration and Guidance: Wayfair provides inspiration and guidance to customers through curated collections, style guides, room ideas, and design tips, helping shoppers visualize and plan their home decor projects, discover new trends, and make informed purchasing decisions.
- Personalized Recommendations: Wayfair offers personalized product recommendations, suggestions, and alerts based on customers’ browsing history, preferences, and past purchases, tailoring the shopping experience to each individual user and enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
Wayfair revenue generation
Wayfair initially operated as a simple drop shipping business but has since diversified its revenue generation strategy.
The company now makes money in the following ways.
Product sales
As an eCommerce giant, Wayfair purchases goods in bulk and then attempts to sell them for a profit.
The company still engages in drop shopping to some extent. When Wayfair receives a customer order, it forwards the order to a partner to fulfill.
The company does not charge partners for sending business their way and even covers shipping costs.
Installation services
Wayfair has partnered with Handy to take the stress out of furniture assembly by connecting consumers with certified installation experts.
The fee for this service varies by product and is split between Handy and Wayfair.
Advertising
Furniture retailers can also buy sponsored ad placements on the Wayfair website.
Ads may be placed preferentially in product search results. They may also be placed in Wayfair video content or via sponsored brand posts.
Wayfair collects advertising revenue based on the number of clicks ads receive. Sponsored posts may attract a fixed fee or a percentage of each subsequent sale.
Interchange fees
Wayfair recently started offering credit cards to consumers with access to perks including cash back rewards, discounts, and no annual fees.
The company makes money whenever a customer purchases with a Wayfair branded Mastercard. This so-called interchange fee is collected by Mastercard from the merchant and is shared with Wayfair.
Credit card interest is also collected if users fail to pay for their orders in full before a designated period. The annual percentage rate (APR) in such a scenario is 26.99%.
Marketing Strategy
- Digital Advertising: Wayfair invests in digital advertising campaigns across various online channels, including search engines, social media platforms, display networks, and affiliate marketing channels, to promote its brand, products, and special offers, targeting relevant audiences and driving traffic to its website.
- Content Marketing: Wayfair produces and distributes content marketing materials, including blog posts, articles, videos, and social media content, that showcase home decor ideas, design inspiration, DIY projects, and product recommendations, engaging and educating customers and driving organic traffic and brand awareness.
- Email Marketing: Wayfair utilizes email marketing campaigns to communicate with customers, deliver personalized recommendations, and promote sales, discounts, and exclusive offers to subscribers, sending targeted email newsletters, alerts, and promotions to drive conversions and repeat purchases.
- Affiliate Partnerships: Wayfair partners with affiliate marketers, influencers, bloggers, and content creators to promote its products and brand through affiliate marketing programs, offering commissions, referral incentives, and co-branded marketing opportunities to affiliates who drive traffic and sales to Wayfair’s website.
- Social Media Engagement: Wayfair engages with customers and followers on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, and Twitter, sharing visual content, user-generated posts, product showcases, and lifestyle inspiration to build community, foster engagement, and increase brand visibility and loyalty.
Distribution Channels
- Website and Mobile App: Wayfair distributes its products and services through its official website and mobile applications for iOS and Android devices, providing customers with a seamless and convenient shopping experience across desktop computers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Third-Party Marketplaces: Wayfair partners with third-party online marketplaces and e-commerce platforms such as Amazon, eBay, Walmart, and Google Shopping to expand its reach and distribution, listing its products for sale on external marketplaces and reaching new customers through additional sales channels.
- Retail Partnerships: Wayfair collaborates with brick-and-mortar retailers, department stores, and home improvement chains to sell its products through physical retail locations, showroom displays, and store-in-store partnerships, extending its reach and brand presence into offline retail channels.
- Direct-to-Consumer Shipping: Wayfair ships products directly to customers’ homes and addresses through its logistics and fulfillment network, offering fast and reliable shipping services, order tracking, and delivery options, ensuring a seamless and efficient shopping experience for online shoppers.
- Global Expansion: Wayfair expands its presence and distribution globally through international shipping, cross-border commerce, and localized websites and platforms, serving customers in key international markets and regions with localized product offerings, pricing, and customer support services.
Key takeaways:
- Wayfair is a North American furniture and household item eCommerce platform. It was founded by Niraj Shah and Steve Conine to give consumers access to greater product diversity in home furnishings.
- Wayfair makes money by purchasing stock in bulk and then selling for a profit. In collaboration with Handy, the company also charges to help customers assemble or install their furniture.
- Wayfair also charges for advertising placements. These may take the form of product search listings, video content, and sponsored brand posts.
Key Highlights
- Introduction:
- Value Proposition and Audience:
- Offers fashionable and accessible luxury products.
- Targets fashion-conscious individuals, brand-conscious consumers, and the youth.
- Core Activities:
- Design: Innovative designers create trendy clothing and accessories.
- Marketing: Effective strategies establish a compelling brand reputation.
- Retail: Operating retail stores and online platforms for product distribution.
- Key Resources:
- Design Team: Creative designers driving innovation and style.
- Brand Heritage: Legacy and reputation enhancing brand appeal.
- Retail Network: Wide network of stores and online presence for accessibility.
- Strategic Partnerships:
- Licensing Partners: Collaborations extending brand influence.
- Influencers Engagement: Leveraging influencers for wider exposure.
- Retail Alliances: Partnerships with retailers expanding product reach.
- Cost Allocation:
- Design Investment: Funds dedicated to creative ingenuity.
- Marketing Budget: Building and nurturing brand identity.
- Retail Operations: Managing stores and online platforms.
- R&D Spending: Staying ahead in the ever-evolving fashion industry.
Read Next: Who Owns IKEA? IKEA Business Model, IKEA Competitors, IKEA Effect, ALDI Business Model, Tesco PESTEL Analysis.
Related: What Is A B2B2C Business Model?
Related To Wayfair






Related Business Model Types




Attention Merchant Business Model










Main Free Guides:









