The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Concept | The Sales Funnel, also known as the purchase funnel or sales pipeline, is a visual representation of the customer journey from initial awareness to making a purchase. It illustrates the stages that potential customers go through as they interact with a business, from the top of the funnel (TOFU) to the bottom of the funnel (BOFU). Understanding and optimizing the sales funnel is crucial for businesses to convert leads into customers effectively. |
| Key Stages | The sales funnel typically consists of the following key stages: – Awareness: At the top of the funnel, potential customers become aware of a product or service through marketing efforts, such as advertising, social media, or content marketing. – Interest: In this stage, prospects show interest and engage with the business by exploring its offerings, visiting the website, or subscribing to newsletters. – Consideration: Prospects evaluate the product or service, comparing it with alternatives and seeking more information. – Intent: At this stage, prospects signal their intent to purchase by requesting quotes, signing up for trials, or adding items to their cart. – Purchase: The final stage is when prospects become customers by completing a purchase or signing a contract. |
| Conversion Rates | The funnel is not linear, and not all prospects progress through all stages. Conversion rates represent the percentage of prospects who move from one stage to the next. Tracking and optimizing these rates is critical for improving the sales process. |
| Application | The sales funnel serves several purposes in business: – Lead Generation: It guides lead generation efforts, helping businesses target and attract potential customers effectively. – Customer Journey Mapping: It helps map out and understand the customer’s path, allowing for tailored marketing and sales strategies. – Sales Forecasting: By tracking conversion rates and the number of leads at each stage, businesses can forecast future sales and revenue. – Optimization: Analyzing the funnel helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement in the sales process. |
| Benefits | Utilizing the sales funnel provides various benefits: – Efficient Resource Allocation: Businesses can allocate marketing and sales resources more efficiently by focusing efforts on stages with lower conversion rates. – Improved Customer Experience: Tailored content and interactions at each stage enhance the overall customer experience. – Higher Conversions: By addressing customer needs and objections at each stage, businesses can increase the likelihood of conversion. |
| Challenges | Challenges associated with the sales funnel include: – Customer Behavior Variability: Different customers progress through the funnel at varying speeds and with different behaviors, making it challenging to create one-size-fits-all strategies. – Data Accuracy: Accurate data collection and tracking are essential for funnel analysis, and errors or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate insights. – Competitive Landscape: External factors, including competitors’ actions and market changes, can impact the funnel and require constant adaptation. |
| Real-World Application | – E-commerce businesses often use sales funnels to guide website visitors from product discovery to checkout. – B2B companies employ sales funnels to manage complex, multi-step sales processes, including lead nurturing and contract negotiation. – Subscription-based businesses use funnels to convert free trial users into paying customers. |
Understanding the Sales Funnel:
- Awareness: This is the top of the funnel, where potential customers become aware of your product or service. It involves marketing efforts to attract a broad audience.
- Interest: In this stage, leads show interest in your offering. They may seek more information, engage with your content, or sign up for newsletters.
- Consideration: Leads in the consideration stage are actively evaluating your product or service. They may compare it with alternatives, read reviews, and engage in deeper research.
- Intent: Intent signifies strong interest and a potential willingness to purchase. Leads in this stage may request quotes, demos, or trials.
- Evaluation: In the evaluation stage, leads thoroughly assess your offering and may engage with sales representatives for discussions and negotiations.
- Purchase: The bottom of the funnel is where leads become customers by making a purchase decision.
Principles of the Sales Funnel:
- Lead Progression: The sales funnel represents the natural progression of leads from initial awareness to conversion. It allows businesses to track and manage this journey.
- Customer-Centric: The funnel helps businesses understand the customer’s perspective, allowing for tailored marketing and sales strategies at each stage.
- Conversion Optimization: Businesses can focus on optimizing conversion rates at each stage to maximize sales efficiency.
- Content Alignment: Content and messaging should align with each stage of the funnel to provide relevant information and nurture leads effectively.
Advantages of the Sales Funnel:
- Visual Representation: The funnel provides a visual representation of the customer journey, making it easier to understand and manage.
- Lead Segmentation: It allows for the segmentation of leads based on their stage in the funnel, enabling personalized communication.
- Conversion Tracking: Businesses can track and analyze conversion rates at each stage to identify bottlenecks and optimize the sales process.
- Resource Allocation: The funnel helps allocate marketing and sales resources effectively by focusing efforts on high-potential leads.
Challenges of the Sales Funnel:
- Complex Customer Journeys: In today’s digital age, customer journeys can be complex, with multiple touchpoints and interactions, making funnel tracking more challenging.
- Individual Variation: Not all leads follow a linear path through the funnel. Some may skip stages or move back and forth.
- Data Accuracy: Maintaining accurate data and tracking leads’ progress can be challenging without the right tools and systems.
- Competition: In a competitive market, businesses need to ensure that their funnel is optimized to retain leads and convert them into customers.
When to Use the Sales Funnel:
- Lead Management: The sales funnel is essential for lead management, helping businesses track, nurture, and convert leads effectively.
- Sales Strategy: It guides the development of sales strategies, enabling businesses to align their efforts with the customer journey.
- Marketing Campaigns: The funnel informs marketing campaigns, ensuring that messaging and content are tailored to each stage.
- Conversion Optimization: Businesses should use the funnel when seeking to improve conversion rates and overall sales efficiency.
What to Expect from Using the Sales Funnel:
- Improved Lead Tracking: Expect enhanced tracking and management of leads as they progress through the funnel.
- Personalized Communication: The funnel enables more personalized communication with leads based on their stage and needs.
- Conversion Optimization: Businesses can expect to see improvements in conversion rates and sales efficiency through funnel optimization.
- Better Resource Allocation: Efforts and resources can be allocated more effectively to high-potential leads.
Long-Term Impact of the Sales Funnel:
- Sales Efficiency: Over time, the sales funnel can lead to increased sales efficiency and higher conversion rates.
- Data-Driven Culture: It fosters a data-driven culture within the organization, leading to better decision-making and strategy development.
- Customer Understanding: The funnel provides insights into customer behavior and preferences, allowing for more customer-centric approaches.
- Competitive Advantage: A well-optimized sales funnel can provide a competitive advantage by streamlining the sales process and improving customer relationships.
Have sales funnels ever existed in the real world?
The sales funnel is just a representation of reality; as such, it has its own drawbacks, such as:
- Assuming most customers reach you through the same path can drive bad marketing campaigns.
- Assuming the sales cycle is linear, when it’s not, it can create the illusion of understanding for the customer.
- Simplifying too much the sales funnel means losing significant opportunities as the service won’t correctly be tailored for more complex shots.
And yet the sales funnel has been a useful tool for marketing and salespeople as a way to communicate and talk about the way customers get to know a brand.
In short, sales funnels introduced a consumer-centered approach to sales that required marketing people to get aligned with potential customers, thus identifying potential actions to take to unlock the potential of a product.
Therefore, the funnel answers an important function: setting a team’s priorities. So even with its evident limitations, it can still be a great tool for teams.
A team’s prioritization tool
A classic example of sales funnel is the AARRR funnel, which is a longer version as it relates to subscription-based or SaaS companies for which the journey of the potential customer starts with the awareness of the brand, and ends with the product referral.

This means that the sales funnel helps the whole team understand the kind of actions to undertake for each step of the journey.
For instance, if the marketing team has identified the problem in the acquisition stage, where only a few contacts get to know the brand, then they will know to leverage certain channels rather than others (for instance, SEO, email marketing, PR, or else, rather than working on-page conversions).
If instead, the marketing team has identified the problem in the activation stage, then other things will need to be prioritized, such as landing page conversions or perhaps product features.
Shortening the sales cycle

One of the elements that, most of all, can damage the bottom line is a mistake in understanding the sales cycle for larger customers.
As sales deals move from small and B2C to larger and more complex deals, the sales cycle becomes increasingly volatile.

Thus, deals that you thought might close in a few weeks, take months, and this, in turn, affects the health of the overall organization.
Therefore, having a sales funnel to prioritize at each step of the cycle can be a critical element in sustaining the company.
In short, if you know that important deals will take closer than expected to close, you will need to fill the so-called sales pipeline quickly to prevent completely missing the targets.

From attention to desire

Sales funnels or mental models like the AIDA model can help salespeople use a common language to understand the potential journey customers are taking.
And it becomes a tool to question whether the lead is ready for conversion. In short, mistaking a lead at the interest stage for the desired stage can lead to misleading action that can wreck the whole relationship with the prospect.
Freeterprise

When marketing works well, it can become an incredible tool in the hands of salespeople to close deals in much less time and to shorten the sales cycle.
Marketing automatons like in freeterprise models can help salespeople identify the right opportunities that can become enterprise accounts for the organization.
The social seller

In the era of digital platforms, sales teams can leverage tools to make the process more effective.
Platforms like LinkedIn are powerful tools for business developers and social sellers.
And they have become indispensable tools for sales teams.
The sales funnel has started to morph into something else, as digital business models took over.
Digital platforms

As digital platforms have become among the dominant players of this era, they also learned to take advantage of intrinsic features of digital spaces, that before would not be available.
Indeed, platforms can leverage network effects, whereas the more users join the more the platform becomes valuable for the users coming next.
With this logic of consolidation of the business infrastructure, marketing teams followed suit.
This means that marketing or sales aren’t necessarily made on a one-to-one basis (complex sales and business deals still are) but that the marketing team becomes more like a policy-making lab, where it needs to experiment with all the sorts of ways to build ecosystems rather than just getting the next customers in.
When companies start to prioritize this strategy, they align their marketing efforts around a platform business model logic.
Customers vs. ecosystems and communities
Many companies we value today have focused their efforts on building ecosystems of a few key players coming together.
When the ecosystem becomes liquid (players interact freely, with a minimum effort from the central platform), the platform has reached its maximum potential.
Therefore, as this happens, marketing becomes the set of activities to help this ecosystem to build up in the first place and to maintain or grow. In that, the marketer becomes more like a policy-maker or a community-builder.
When a company creates an ecosystem, it becomes possible to convert its business model, relatively quickly.
See how Airbnb is during the pandemic times, trying to convert from physical and local experiences to digital experiences.

As the effects of the pandemic on Airbnb’s business model ended, Airbnb shifted again to its growth engine, and it turned out to be a much stronger company than before!

Flywheels and momentum

When Jeff Bezos scratched on a piece of paper what would become the Amazon Flywheel (at Amazon, they called it a virtuous cycle), this was a way to align the marketing effort with the fact that Amazon was transitioning at all effects to consolidate its e-commerce platform (so enable third-party stores to sell on Amazon, which as a side-effect brought to the birth of another platform: Amazon AWS).

Other examples, like the Etsy business model, also follow the same logic.
As the flywheel model gains momentum, you don’t start from scratch, but when the accumulated momentum reaches a critical mass as a side effect, an entrepreneurial ecosystem forms, which becomes the most important asset for the platform business model.
Therefore, marketing at this level becomes a completely different game.

Other examples, like the Uber business model, also combine platform (both business and technical) and marketing efforts to build momentum.
The argument from a company like Uber is that when the ecosystem becomes liquid, this creates s market which is much larger than the previous one:

At each expansion stage, the next market created is much bigger than the previous, and as a result, the platform scales with it.
By scaling with the market, the whole context changes, and the whole company changes with it, thus requiring a new business model.
Case Studies
E-commerce:
Fashion Retail Sales Funnel:
- Discovery: Customers discover clothing items through online ads, social media, or website search.
- Selection: They select products, view product details, and add desired items to their shopping cart.
- Checkout: Customers proceed to checkout, enter shipping and payment information, and review their order.
- Purchase: They complete the purchase, receiving an order confirmation and tracking details.
Electronics Store Sales Funnel:
- Research: Shoppers research electronic gadgets, comparing specifications and reading customer reviews.
- Selection: After choosing products that fit their needs, they add items to the cart.
- Checkout: Customers go to the checkout page, where they provide shipping and payment details.
- Purchase: They finalize the purchase, receiving an order confirmation and delivery updates.
Beauty Products Sales Funnel:
- Exploration: Beauty enthusiasts explore skincare and makeup products through brand websites and beauty influencers.
- Selection: They select products based on their needs, adding them to their online shopping cart.
- Checkout: Customers proceed to the checkout, entering delivery information and payment details.
- Purchase: They complete the purchase, receiving a confirmation email and shipping notifications.
Home Decor Sales Funnel:
- Inspiration: Homeowners and decorators seek inspiration on home decor websites, social media, or in-store displays.
- Selection: After choosing decor items, they add them to their virtual shopping cart.
- Checkout: Customers proceed to checkout, providing shipping and payment information.
- Purchase: They finalize the purchase, receiving confirmation and delivery updates.
Subscription Services:
Streaming Services Sales Funnel:
- Sign-up: Users sign up for streaming platforms, providing email addresses and creating accounts.
- Free Trial: They enjoy a free trial period with access to premium content.
- Subscription: Customers subscribe to premium plans, providing payment details.
- Continued Streaming: Users continue streaming content, with subscriptions auto-renewing until canceled.
Meal Kit Delivery Sales Funnel:
- Exploration: Foodies explore meal kit options online, selecting preferred meal plans.
- Customization: They customize ingredients and dietary preferences for their meal kits.
- Subscription: Customers subscribe to meal kit services, with recurring deliveries scheduled.
- Regular Deliveries: Subscribers receive regular deliveries of meal kits per their chosen schedule.
Magazine Subscription Sales Funnel:
- Interest: Readers discover magazines through advertisements or online recommendations.
- Selection: They choose subscription packages (e.g., digital, print, or both).
- Payment: Customers make payments for the selected subscription plan.
- Monthly Issues: Subscribers receive monthly issues or access digital content as part of their subscription.
Education and Training:
University Enrollment Sales Funnel:
- Exploration: Prospective students research universities, explore programs, and visit campus websites.
- Application: They complete university applications, providing academic records and personal information.
- Acceptance: Students receive acceptance offers from the university.
- Enrollment: Accepted students enroll in programs, pay tuition, and attend classes.
Online Tutoring Sales Funnel:
- Inquiry: Parents or students inquire about online tutoring services.
- Scheduling: They schedule tutoring sessions based on availability and subject requirements.
- Learning: Students attend online tutoring sessions, receiving academic support.
- Ongoing Sessions: Learners continue attending sessions as needed to achieve academic goals.
Language Learning App Sales Funnel:
- Download: Language learners download language learning apps from app stores.
- Trial: Users complete free trial lessons, experiencing the app’s language learning features.
- Subscription: Customers subscribe to premium plans with access to advanced language courses.
- Skill Improvement: Subscribers use the app to improve language skills through structured lessons.
Key takeaways
- Sales funnels are useful tools that enable sales and marketing teams to prioritize their work.
- While sales funnels are useful for digital and platform business models, the flywheel can be more effective.
- Indeed a flywheel marketing model can help build an ecosystem that becomes the main asset of the platform.
Key Highlights:
- Sales Funnel Overview:
- Representation vs. Reality:
- The sales funnel is a simplified representation of the customer journey and has limitations, including assuming a linear sales cycle and a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Consumer-Centered Approach:
- Sales funnels introduced a consumer-centric approach, aligning marketing efforts with potential customers and identifying actions to unlock a product’s potential.
- Team Prioritization Tool:
- Sales funnels help teams prioritize actions at each stage of the customer journey based on identified issues or challenges.
- AARRR Funnel:
- The AARRR funnel is an extended version of the sales funnel, particularly relevant for subscription-based or SaaS companies, covering stages from awareness to product referral.
- Shortening the Sales Cycle:
- Understanding the sales cycle, especially for larger customers, is critical to preventing delays in closing deals.
- Sales funnels help prioritize actions and fill the sales pipeline.
- AIDA Model:
- Freeterprise Model:
- Freeterprise combines free and enterprise models, with free users converted into enterprise accounts by sales teams using marketing automation.
- Social Selling:
- Social selling involves developing trust and rapport with prospects through online platforms like LinkedIn, enhancing the sales cycle’s effectiveness.
- Digital Platforms and Ecosystems:
- Digital platforms leverage network effects and ecosystem building, leading to a shift in marketing’s role from acquiring customers to ecosystem development.
- Flywheels and Momentum:
- Flywheel models like Amazon’s Virtuous Cycle focus on customer experience, driving platform growth and creating entrepreneurial ecosystems.
- Uber’s example shows how a scaling market can necessitate a new business model.
- Key Takeaways:
- Sales funnels are valuable for prioritizing sales and marketing efforts.
- For platform-based businesses, the flywheel model can be more effective in building and sustaining ecosystems.
- Marketing plays a crucial role in ecosystem development and platform scaling.
Sales Funnel Types Case Studies
| Scenario | Description | Implications | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce Sales Funnel | In e-commerce, the Sales Funnel outlines the stages a website visitor goes through from browsing to making a purchase, including product discovery, adding items to the cart, and completing the checkout process. | – Identifies drop-off points and areas for website optimization. – Guides retargeting and abandoned cart email campaigns. – Helps forecast sales revenue and set conversion goals. | Example: An online clothing store’s Sales Funnel includes website visitors, product viewers, cart additions, and completed purchases. |
| B2B Sales Funnel | In B2B sales, the Sales Funnel represents the journey of a business customer, from initial contact or lead generation to deal closure and contract signing, with stages like lead, prospect, proposal, and negotiation. | – Supports lead scoring and prioritization of high-value leads. – Aids in pipeline management and sales forecasting. – Assists in identifying bottlenecks and improving sales processes. | Example: A software company’s B2B Sales Funnel includes leads generated through website forms, followed by prospecting, product demos, proposals, negotiations, and contract closures. |
| SaaS Subscription Funnel | SaaS companies use the Sales Funnel to illustrate the process of acquiring and retaining subscription customers, starting with sign-ups or free trials and progressing through onboarding, activation, and subscription renewals. | – Helps analyze user behavior and optimize onboarding experiences. – Guides efforts to reduce churn and increase customer engagement. – Provides insights into user segmentation and feature adoption. | Example: A cloud-based project management tool’s Sales Funnel begins with free trial sign-ups, followed by trial usage, activation, subscription conversions, and ongoing renewals. |
| Real Estate Sales Funnel | In real estate, the Sales Funnel represents the steps a potential homebuyer takes, starting with property search and inquiry, proceeding to property viewing, offers, negotiations, and closing the sale. | – Assists in tracking leads and managing buyer-agent relationships. – Helps real estate agents understand buyer intent and preferences. – Guides marketing efforts for property listings and open houses. | Example: A real estate agency’s Sales Funnel tracks leads generated from online listings, inquiries, property showings, offers, counteroffers, and final sale agreements. |
| Lead Generation Funnel | Lead generation funnels are often used in marketing to illustrate the process of turning website visitors or social media users into leads through content marketing, email capture, and lead nurturing, leading to sales conversions. | – Informs content creation and email marketing strategies. – Measures lead quality and conversion rates. – Enables continuous optimization of lead generation efforts. | Example: A digital marketing agency’s Lead Generation Funnel begins with website traffic, followed by lead capture through gated content, lead nurturing emails, and conversion into paying clients. |
| Related Frameworks | Description | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| AIDA Model | – Describes the stages a customer goes through in the purchasing process: Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. AIDA helps marketers and sales professionals understand and guide consumers through the sales funnel. | – When developing marketing or sales strategies. – Mapping out customer journey stages to create targeted messaging and promotional campaigns that guide prospects toward making a purchase. |
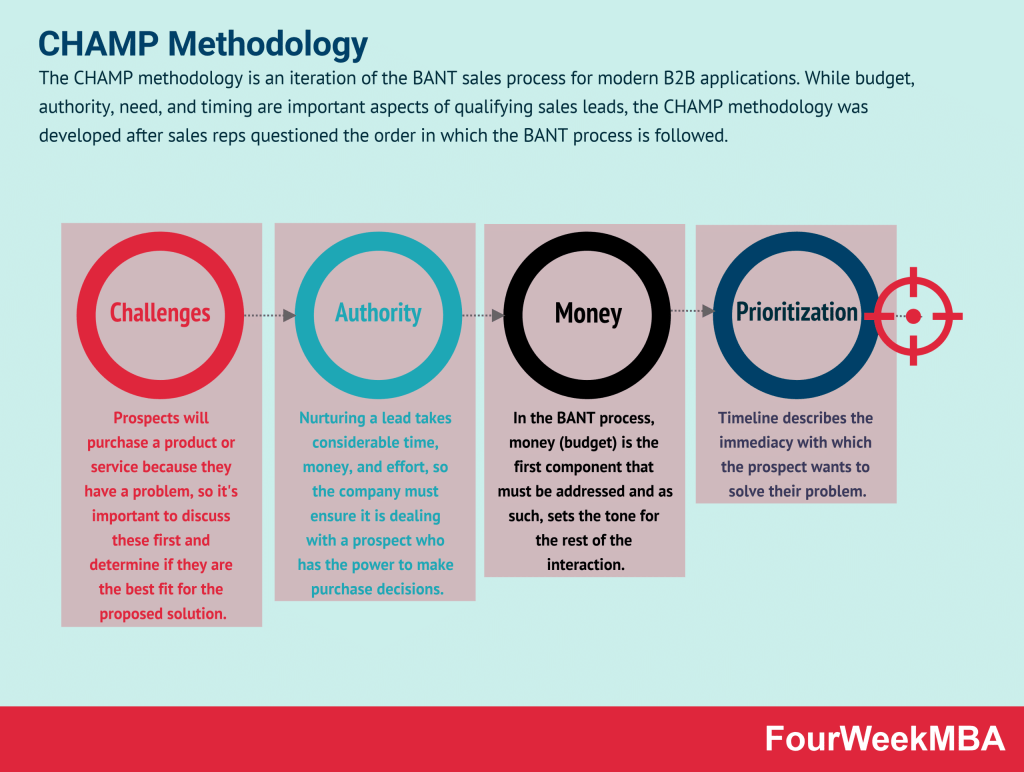
| BANT Criteria | – Stands for Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline, used to qualify leads and prioritize sales efforts. BANT Criteria helps sales teams focus on prospects with the highest likelihood of conversion. | – When qualifying leads or prioritizing sales opportunities. – Assessing prospects based on their budget, decision-making authority, need for the product or service, and timeframe for purchase to allocate resources effectively. |
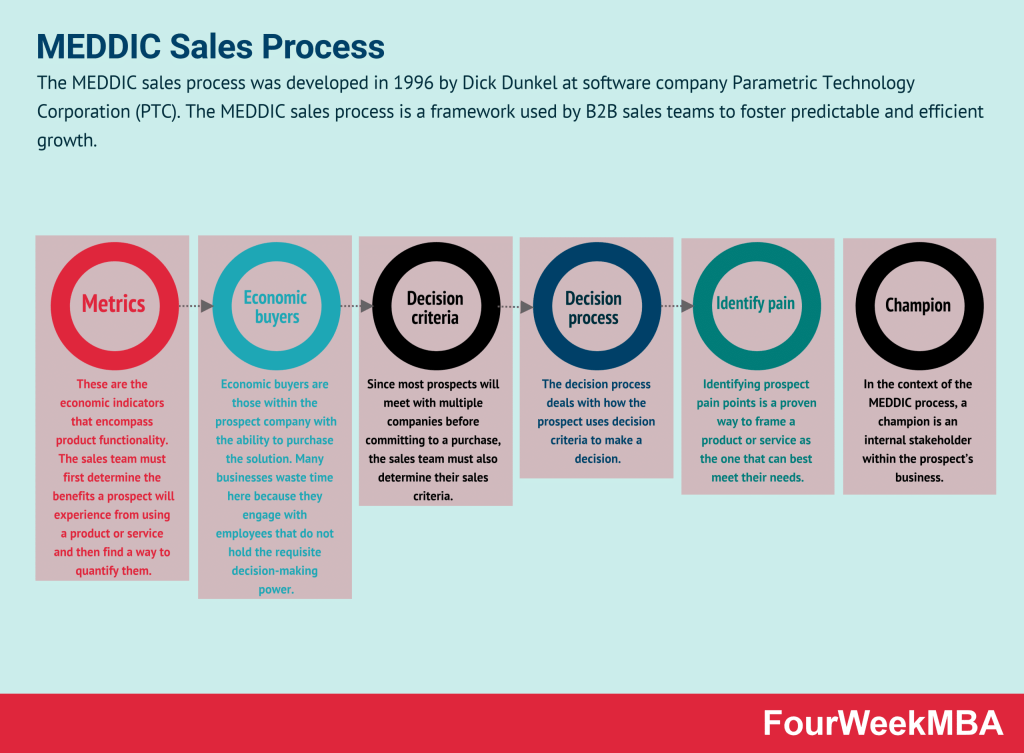
| SPIN Selling | – Focuses on asking situational, problem, implication, and need-payoff questions to uncover customer needs, address pain points, and provide tailored solutions. SPIN Selling emphasizes consultative selling and relationship-building. | – When engaging in complex B2B sales or consultative selling. – Using a structured questioning approach to understand customer challenges, build rapport, and offer solutions that align with their needs and objectives. |
| Solution Selling | – Involves identifying customer pain points and offering solutions that address their specific needs and objectives. Solution Selling emphasizes value proposition, relationship-building, and problem-solving. | – When selling complex or customizable products or services. – Tailoring sales pitches and proposals to demonstrate how the offered solution addresses the customer’s unique challenges and delivers measurable value. |
| Customer Journey Mapping | – Visualizes the stages and touchpoints a customer goes through when interacting with a brand or making a purchase decision. Customer Journey Mapping helps organizations understand customer experiences and identify opportunities for improvement. | – When analyzing and optimizing the customer experience. – Mapping out customer interactions across channels and touchpoints to identify pain points, gaps, and areas for enhancement throughout the sales funnel. |
| Lead Scoring | – Assigns numerical values to leads based on their characteristics, behaviors, and engagement levels to prioritize follow-up and tailor sales efforts. Lead Scoring helps sales teams focus on leads with the highest potential for conversion. | – When managing and qualifying leads in a CRM system. – Developing lead scoring criteria and algorithms to prioritize sales outreach and allocate resources effectively based on lead quality and likelihood of conversion. |
| Challenger Sale Model | – Proposes that successful sales professionals challenge customers’ assumptions, teach them something new, tailor solutions to their needs, gain consensus among stakeholders, and drive results. The Challenger Sale Model emphasizes insights-based selling and commercial teaching. | – When engaging with knowledgeable and skeptical buyers. – Providing insights, challenging assumptions, and guiding customers through the decision-making process to differentiate offerings and create value. |
| Inbound Marketing | – Focuses on attracting and engaging prospects through valuable content, personalized experiences, and relationship-building techniques. Inbound Marketing aligns with the modern buyer’s preference for self-directed research and engagement. | – When building brand awareness and generating leads. – Creating and distributing relevant and helpful content to attract, engage, and nurture prospects throughout their journey, from awareness to purchase and beyond. |
| Account-Based Marketing (ABM) | – Targets high-value accounts or companies with personalized marketing and sales efforts tailored to their specific needs and preferences. Account-Based Marketing fosters deeper relationships and alignment between marketing and sales teams. | – When pursuing strategic or enterprise-level accounts. – Collaborating with marketing and sales teams to develop and execute personalized campaigns and outreach strategies that resonate with target accounts and decision-makers. |
| Cross-Selling and Upselling | – Involves offering additional products or services (upselling) or complementary items (cross-selling) to existing customers to increase their lifetime value and maximize revenue. Cross-Selling and Upselling leverage customer relationships and understanding to drive incremental sales. | – When engaging with existing customers or clients. – Identifying opportunities to recommend related or upgraded offerings that enhance the value of the initial purchase and meet evolving needs or preferences. |
Related Business Concepts






















Palantir Acquire, Expand, Scale Framework



Read: product development frameworks here.
Read Next: SWOT Analysis, Personal SWOT Analysis, TOWS Matrix, PESTEL Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, TOWS Matrix, SOAR Analysis.
Main Free Guides:









