New Product Development

BCG Matrix

Ansoff Matrix

User Experience Design

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Empathy Mapping

Perceptual Mapping

Value Stream Mapping

Eisenhower Matrix

MoSCoW Method

Scaled Agile

Kanban Framework

Minimum Viable Product

Lean MVP

Design Thinking

Jobs-To-Be-Done

SWOT Analysis

TOWS Matrix

Pirate Metrics

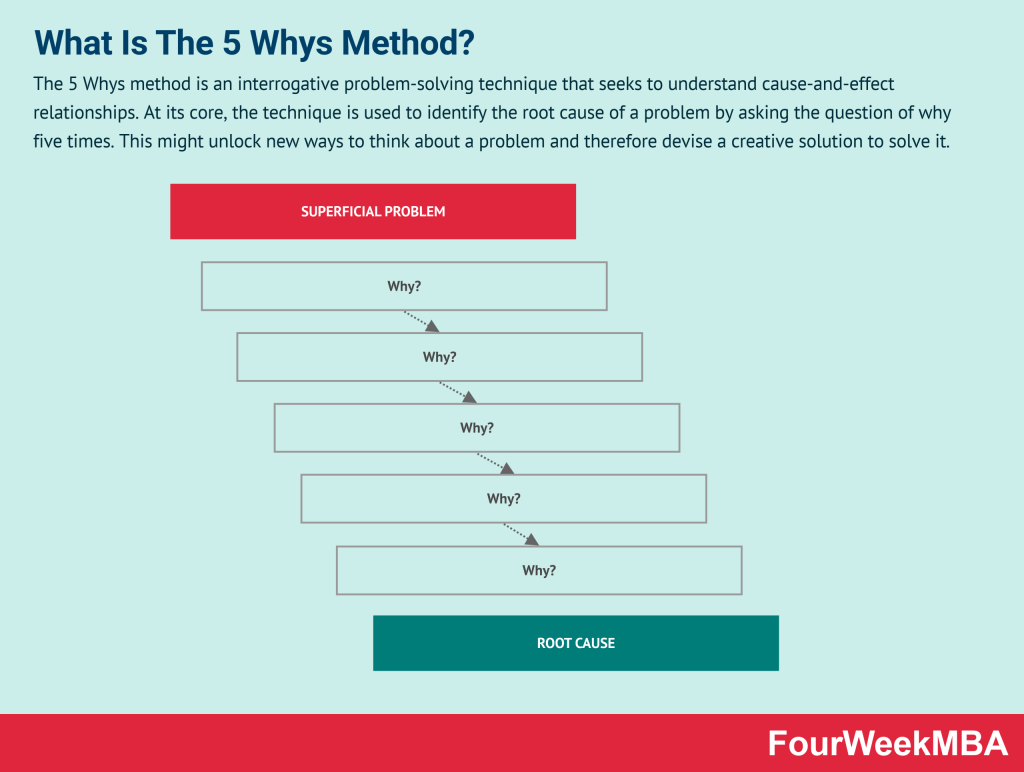
5 Whys Method
Agile Project Management

Blue Sea Strategy

Minimum Viable Audience

Business Engineering Framework

Highlights
| Concept | Description | When to Use | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Product Development | A process that includes steps from idea generation to post-launch review, aiming to analyze and launch new products. | When developing and launching new products or services. | Ensures a systematic approach to innovation. | May be time-consuming and resource-intensive. |
| BCG Matrix | A product portfolio analysis framework categorizing products into cash cows, pets, question marks, and stars. | When evaluating and managing a product portfolio based on growth and market share. | Provides a visual overview of product performance. | May oversimplify complex product dynamics. |
| Ansoff Matrix | A strategic framework categorizing growth strategies based on market and product characteristics. | When deciding on growth strategies, considering market and product factors. | Helps align strategies with market conditions. | May not cover all aspects of strategy development. |
| User Experience Design | A process used by design teams to create products that are useful and relevant to consumers. | When designing products or services with a focus on user satisfaction and usability. | Improves user satisfaction and product adoption. | Requires user research and iterative design. |
| Cost-Benefit Analysis | An analysis process to evaluate decisions by comparing costs and benefits, helping with project planning and assessment. | When assessing project feasibility, investment decisions, and resource allocation. | Provides a structured approach to decision-making. | May involve complex cost and benefit estimation. |
| Empathy Mapping | A visual representation of user behavior and attitudes to gain insights into user experiences and needs. | When seeking a deeper understanding of user perspectives and improving user-centered design. | Enhances user-centered design processes. | Requires effective data collection and interpretation. |
| Perceptual Mapping | A visual representation of consumer perceptions of brands, products, or services to assess their relative positions. | When analyzing brand or product positioning and comparing consumer perceptions. | Provides insights into brand or product perception. | May be subjective and dependent on consumer data. |
| Value Stream Mapping | A flowchart-based method to analyze and improve the delivery of products and services by identifying value streams. | When optimizing processes and enhancing the delivery of products and services. | Identifies process bottlenecks and inefficiencies. | Requires a deep understanding of value stream concepts. |
| Eisenhower Matrix | A tool for prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance, helping to focus on critical activities. | When prioritizing tasks and time management to maximize productivity. | Focuses attention on critical and important tasks. | May not account for varying task complexities. |
| MoSCoW Method | A task prioritization framework based on categories (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) to manage tasks. | When prioritizing tasks and requirements within a project, especially with limited resources. | Helps clarify task priorities and expectations. | May require consensus among stakeholders. |
| Scaled Agile | A framework (SAFe) designed for large organizations to implement agile practices at an enterprise scale. | When large organizations need to adopt agile methodologies and manage complex projects. | Enables agile practices at an organizational level. | May require significant organizational change. |
| Kanban Framework | A lean manufacturing framework for visualizing work, optimizing processes, and improving product delivery. | When optimizing workflows, reducing bottlenecks, and improving product delivery. | Enhances visibility and efficiency in workflow management. | May not address broader strategic aspects. |
| Minimum Viable Product | A version of a new product that allows teams to collect customer insights with minimal effort, following lean startup principles. | When developing products to validate customer needs efficiently. | Reduces development risk and time. | May lack advanced features initially. |
| Lean MVP | An approach where market risk is validated before proceeding with minimum viable product development. | When seeking to minimize market risk and validate ideas before full product development. | Reduces the risk of building unwanted products. | May extend the validation phase. |
| Design Thinking | An approach to innovation that integrates user needs, technology possibilities, and business success into product design. | When solving complex problems and developing innovative solutions. | Balances desirability, feasibility, and viability. | Requires a collaborative and iterative process. |
| Jobs-To-Be-Done | A framework for understanding consumer needs based on the idea that products are purchased to get specific jobs done. | When categorizing, capturing, and organizing consumer needs for product development. | Focuses on enduring consumer needs and motivations. | Requires in-depth customer research and analysis. |
| SWOT Analysis | A framework for evaluating a business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to inform strategic planning. | When conducting strategic analysis and decision-making for businesses. | Provides a structured approach to strategic assessment. | May be subjective and dependent on data quality. |
| TOWS Matrix | A variation of the SWOT Analysis that focuses on addressing relationships between Threats, Opportunities, Weaknesses, and Strengths. | When seeking a more comprehensive view of strategic options and actions. | Highlights strategic connections between factors. | Requires careful consideration of relationships. |
| Pirate Metrics | A simplified model (AARRR) to understand and track user paths toward becoming customers and brand referrers. | When analyzing user behavior and engagement in conversion funnels. | Offers a concise framework for growth analysis. | May not capture all nuances of user behavior. |
| 5 Whys Method | An interrogative problem-solving technique that seeks to identify the root cause of a problem by asking “why” five times. | When investigating the underlying causes of complex problems to find creative solutions. | Helps uncover hidden causes and solutions. | May require deeper analysis beyond five whys. |
| Agile Project Management | A strategy that breaks large projects into smaller, manageable tasks and completes them in iterations. | When managing projects with changing requirements, focusing on adaptability and customer feedback. | Enhances adaptability and customer satisfaction. | May require ongoing iterations and adjustments. |
| Blue Sea Strategy | A strategic framework that aims to create uncontested market spaces by differentiating from existing competition. | When developing strategies for innovation and market disruption. | Focuses on creating unique value and reducing competition. | Requires innovative thinking and execution. |
| Minimum Viable Audience | Represents the smallest audience that can sustain a business, emphasizing finding unmet needs within existing markets. | When identifying niche markets and unmet customer needs in the early stages of a business. | Focuses on specific and underserved customer segments. | May limit growth beyond the minimum audience. |
| Business Engineering Framework | A comprehensive approach that combines entrepreneurship, strategy, and scaling concepts to drive business innovation. | When seeking a systematic framework for business model innovation and scaling. | Integrates various aspects of business innovation. | Requires deep understanding and implementation. |
Main Free Guides:









