Venmo is a peer-to-peer payments app enabling users to share and make payments with friends for a variety of services. The service is free, but a 3% fee applies to credit cards. Venmo also launched a debit card in partnership with Mastercard. Venmo got acquired in 2012 by Braintree, and Braintree got acquired in 2013 by PayPal.
| Elements | Analysis | Implications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peer-to-Peer Payments | Venmo offers a peer-to-peer (P2P) payment platform that allows users to send money to friends and family quickly and easily through their mobile devices. | Facilitates convenient and secure money transfers between individuals. Enhances social interactions and eliminates the need for cash transactions. Attracts a user base looking for P2P payment solutions. | Users can send money to friends for shared expenses, such as dining, entertainment, or rent, using the Venmo app, making transactions simple and cashless. |
| Mobile Payment App | Venmo operates primarily as a mobile payment app, available for iOS and Android devices. Users link their bank accounts or credit/debit cards to Venmo for seamless transactions. | Provides users with a convenient and accessible payment tool on their smartphones. Enables easy integration with existing financial accounts. Encourages mobile-first payment behavior. | Users can download the Venmo app, link their preferred payment methods, and use it to make payments, split bills, or request money from their contacts, all from their mobile devices. |
| Social Integration | Venmo incorporates a social feed feature that allows users to share their transactions and interact with friends by adding comments and emojis. The social aspect adds an element of fun and engagement to payments. | Enhances the user experience by making payments a social activity. Drives user engagement and encourages regular app usage. Creates network effects as users invite friends to join Venmo. | Users can see their friends’ transactions and leave comments or emojis on payments in their Venmo feed, making payments more interactive and enjoyable. |
| Payment Card | Venmo offers a physical payment card, known as the Venmo Debit Card, which is linked to users’ Venmo accounts and allows them to make purchases at physical stores and withdraw cash from ATMs. | Expands Venmo’s usability beyond digital transactions to physical retail locations. Provides a physical representation of the digital wallet. Encourages users to use Venmo for everyday spending. | Users can request and use the Venmo Debit Card for in-store purchases and cash withdrawals, making their Venmo balance accessible in the physical world. |
| Business Partnerships | Venmo partners with various businesses to enable users to make payments within popular apps and websites. These partnerships enhance Venmo’s ecosystem and extend its reach to e-commerce and other industries. | Increases Venmo’s utility by allowing users to make payments within partner apps and websites. Drives adoption and usage among partner businesses’ customer bases. Boosts Venmo’s transaction volume. | Users can use Venmo to pay for services and products within partner apps and websites, such as Uber, Grubhub, and many online retailers. |
| In-App Purchases | Venmo allows users to shop and pay for products directly within the app through partnerships with e-commerce platforms. Users can discover and buy items, making the app a shopping and payment hub. | Expands Venmo’s offerings to include shopping capabilities, creating a comprehensive financial ecosystem. Increases user engagement by providing a one-stop solution for payments and shopping. | Users can browse and buy products from various merchants within the Venmo app, making payments for online shopping more convenient. |
| Value Proposition | Venmo’s value proposition centers on providing users with a user-friendly and social P2P payment platform that simplifies money transfers, enhances social interactions, and offers additional financial services such as in-app shopping and the Venmo Debit Card. | Offers users a convenient, social, and comprehensive financial solution for P2P payments and more. Enhances the ease of money transfers and provides a seamless integration of social and financial activities. | |
| Customer Segments | Venmo serves a wide range of customer segments, including individuals who want a convenient P2P payment solution, social users looking to engage with friends through payments, and shoppers who seek an integrated payment and shopping experience. | Addresses the diverse needs and preferences of users seeking a mobile payment app with various features. Captures a user base interested in social interactions, mobile payments, and digital shopping. | |
| Distribution Strategy | Venmo distributes its services primarily through mobile app stores, making the app accessible to iOS and Android users. The Venmo Debit Card is distributed physically, while partnerships with businesses expand its reach further. | Ensures widespread accessibility to the Venmo app through mobile devices. The Venmo Debit Card is physically distributed to users. Partnerships with businesses enable in-app and online payments. | |
| Competitive Advantage | Venmo’s competitive advantage lies in its user-friendly mobile app, social payment features, seamless integration of payment and shopping, and a strong user base. Venmo’s focus on social engagement sets it apart in the P2P payment industry. | Offers a distinct social payment experience that appeals to users seeking both convenience and social interaction. Leverages a strong user base and strategic partnerships to maintain competitiveness. |
Who owns Venmo? Inside PayPal “Payment Platform”
Read Next: How Does PayPal Business Model
Why is Venmo free?
Venmo generates revenue through transaction fees. While most free-to-use mobile apps turn to advertisements for revenue purposes, Venmo has managed to avoid this path.
In a way, Venmo can afford to be free as part of the PayPal ecosystem. In fact, Venmo is the mobile app that allows PayPal to enter a market, those of the millennials.
Is Venmo safe?
After several complaints about how the company handled privacy disclosures, there was a settlement with PayPal, as reported by Tech Crunch.
As claimed by Venmo in terms of security, “Your personal and financial data is encrypted and protected on our secure servers to guard against unauthorized transactions.”
Read Next: How Does PayPal Business Model
The P2P transactions industry in a nutshell
Transaction revenues grew more slowly than both TPV and number of payment transactions in 2017 due primarily to a higher proportion of person-to-person (“P2P”) transactions, primarily from our PayPal and Venmo products from which we earn lower rates and foreign exchange hedging losses. The percentage growth in transaction revenues was lower than the percentage growth in TPV and payment transactions in 2016 primarily due to a higher proportion of P2P transactions (including our Venmo products) for which we earn lower rates, and a higher portion of TPV generated by large merchants who generally pay lower rates with higher transaction volume. The impact of increases or decreases in prices charged to our customers did not significantly impact transaction revenue growth in 2017 or 2016 .
Even though the margins on P2P transactions have lower rates and carry foreign exchange hedging losses compared to large merchants accounts which make up most of the so-called Total Payment Volume (this is a key financial metric for PayPal long-term success), the P2P market is massive:

As reported by emarketer.com:
The use of mobile peer-to-peer (P2P) payment apps such as Venmo in the US will continue to grow by double digits through 2021, according to eMarketer’s latest mobile banking and payments forecast.
Thus, besides the current amount of revenue provided by Venmo to affect PayPal’s bottom line, the strategic importance of this mobile app will also have a long-term financial impact.
Venmo origin story
As recounted by Andrew Kortina, Venmo co-founder via kortina.nyc:
We noticed that we were still using cash and checks to pay each other back and thought this was silly. Everyone should be using PayPal to pay each other back, but no one we knew was. We thought something must be not quite right about the PayPal experience for casual use, and we decided to design something that felt “right,” something that felt consistent with all of the other mobile tools we used to interact with our friends, like SMS, Gmail, Facebook, etc.
As roommates at the University of Pennsylvania in 2001 with Iqram Magdon-Ismail, a friendship was born.
During my senior year, Iqram and Andrew built their first real project; a college classifieds site called My Campus Post.
Then, the two started to build websites for local small businesses, at any price that would allow them to survive.
It was a real door-to-door selling experience that taught them about rejection and how to make things work.
After that, they joined an NYC-based company called iminlikewithyou.com, which Y Combinator-backed.
When the company pivoted to become a games company, the two young men left and temporarily split.
Iqram Magdon-Ismail joined Ticketleap as the VP of Engineering for a few years. Andrew Kortina bounced around and spent time working at Betaworks on Bit.ly.
They knew they wanted to do something together. They just didn’t know yet what would become their next venture.
When they browsed several ideas, they also thought of a music app. This is a scatch of the music app idea shared by Andrew Kortina via kortina.nyc:

Until finally, the idea of Venmo came about:

Source: kortina.nyc
This is how Venmo’s unique value proposition was drafted.
What happened next?
When “Venmo me” became a verb
Today Venmo is quite popular among millennials. It is also interesting to see how the company name over time evolved to become the verb “Venmo me:”

Example of how “venmo me” has become a verb in the US culture and across several states.
Of course, having your company name become a verb doesn’t guarantee success.
Yet, we know that when that happens, that company is close to becoming a cult.
Like when Google became a verb, “google it.”There can’t be any comparison yet between Venmo and Google as verbs:

Comparison between “Venmo me” and “google it” according to Google trends.
You can see how Google is a cult on the web.
However, it is interesting to see how Venmo is trying to become a mainstream phenomenon in the transaction space, at least in the US.
How did they do it?
Branding campaigns to make Venmo into a cult
The success of a brand name at the point of having it join the everyday language isn’t – I argue – something that you can predict or plan.
However, you can help it through a dedicated branding campaign.
Venmo has been pushing a lot with some effective branding campaigns to transform its name into a verb:
Venmo “Blank Me” campaign

Source: brandchannel.com
Some interesting Venmo campaigns are funny and compelling:
Let’s not make it awkward, just ___ me,” and “If you ___ the wrong person tonight, you’ll regret it in the morning,
Venmo voice search command for Siri
Just like Google is continuing millions of people to talk with its voice assistants with a simple command that says “Hey, Google!”
Venmo is using a similar strategy for Siri, the voice assistant for Apple devices:
Make the brand Venmo fresh, fun, and cool
Other branding campaigns have been used to address millennials:
Why do millennials like it so much? As reported by millennials interviewed via clickondetroit.com:
“Venmo has essentially eliminated the use of checks for our generation,”
said recent Michigan State University graduate Nick Bognar.
“Having the ability to immediately pay a friend at dinner or split a bill with roommates over the phone is extremely convenient.”
Bognar, 25, said the social aspect of Venmo is a huge selling point.
“I also enjoy the network effect they have created. Venmo has a live feed similar to your Facebook timeline, and I can quickly see my friends paying each other,” Bognar said.
How much money does Venmo make?
As we’ve seen, Venmo is now part of the product offering for PayPal. Thus, although we don’t have any sales breakdown.
As highlighted by Dan Schulman, President & CEO, in the October 2019 earning transcript:
Venmo continues to be an incredibly powerful platform for engaging consumers. We processed more than $27 billion in volume for the quarter, growing 64%. That’s almost $300 million in payments per day and an annual run rate that now exceeds $100 billion. The Venmo team has made tremendous strides in enhancing the use cases of Venmo including a recently signed deal with Synchrony to provide a Venmo credit card. All of this is producing very strong monetization results. We ended Q3 with Venmo just shy of a $400 million annual revenue run rate.
Even though P2P transactions might have lower margins for PayPal, they bring benefits concerning market reach, product offering, and brand recognition.
Indeed, as of 2019, Venmo is not profitable yet, and its user base might be around 40 million digital users, as reported by CNBC.
How does Venmo work?
Whit Venmo, you can primarily perform a few activities like:
- Make and Share Payments
- Connect with people
- Make purchases
- Quickly transfer money to your bank
As claimed on the Venmo website:
Pay family and friends with Venmo accounts using a phone number or email. If they don’t have a Venmo account, they’ll just need to create one. Find friends automatically by syncing your Facebook or phone contacts.
Venmo is free unless you pay with credit cards:
When you send money using your Venmo balance, bank account, debit card or prepaid card, we waive fees so it’s free. Our standard 3% fee applies to credit cards. Receiving money and making purchases in other apps is always free.
Key takeaways
- Venmo is a peer-to-peer mobile app, trendy among millennials, and part of the PayPal ecosystem.
- Its popularity is also based on the ability of the company to make its name become a verb among millennials.
- The app also allows PayPal to enhance its product offering and make it more suited for younger generations.
- Venmo and other apps, part of the PayPal ecosystem, has taken over the peer-to-peer transaction industry.
Key Highlights
- Venmo Overview:
- Venmo is a peer-to-peer payments app that enables users to make payments and share money with friends for various services.
- Venmo is part of the PayPal ecosystem and was acquired by Braintree in 2012, which was then acquired by PayPal in 2013.
- The app offers a debit card in partnership with Mastercard.
- Ownership and PayPal:
- Revenue Model:
- Safety and Security:
- Venmo claims to encrypt and protect users’ personal and financial data on secure servers to prevent unauthorized transactions.
- P2P Transactions and Growth:
- Venmo’s Origin:
- Venmo was founded by Andrew Kortina and Iqram Magdon-Ismail.
- The idea for Venmo came from a desire to create a mobile payment solution that felt consistent with other communication tools.
- Venmo’s Popularity and Branding:
- Venmo has become popular among millennials and is often used as a verb (“Venmo me”) in everyday language.
- Venmo has launched branding campaigns to make its name synonymous with mobile payments.
- Monetization and Growth:
- Functionality:
- Venmo enables users to make payments, connect with friends, make purchases, and transfer money to their bank accounts.
- It offers fee waivers for payments from Venmo balance, bank account, debit card, or prepaid card, with a 3% fee for credit card payments.
- Key Takeaways:
- Venmo’s integration within the PayPal ecosystem has been a successful strategy for both companies.
- The app’s popularity among millennials and its use as a verb highlight its cultural impact.
- P2P transactions, including Venmo, have transformed the peer-to-peer payments industry and contributed to PayPal’s growth.
Other handpicked related business models:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
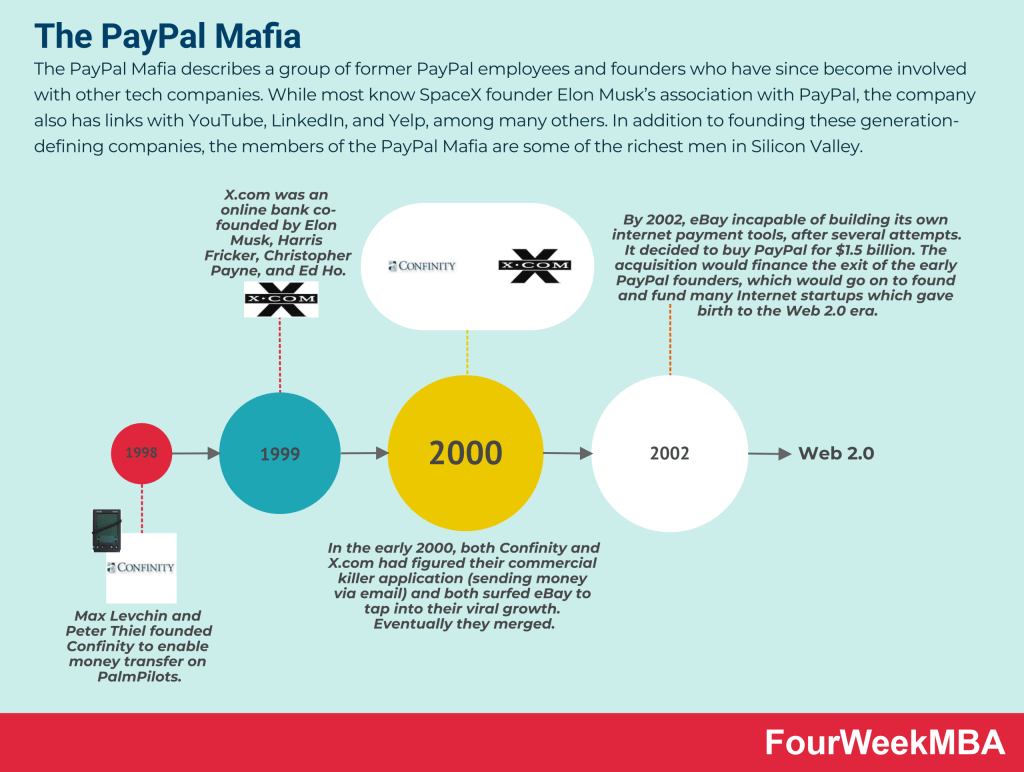
- How Does PayPal Make Money? The PayPal Mafia Business Model Explained
- How Does Twitter Make Money? Twitter Business Model In A Nutshell
- How Does DuckDuckGo Make Money? DuckDuckGo Business Model Explained
- How Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a Nutshell
- How Does Netflix Make Money? Netflix Business Model Explained
- How Does WhatsApp Make Money? WhatsApp Business Model Explained
- The Power of Google Business Model in a Nutshell
Related to PayPal








PayPal Transactions Per Active Users

Read More: How Does TD Ameritrade Make Money, How Does Dave Make Money, How Does Webull Make Money, How Does Betterment Make Money, How Does Wealthfront Make Money, How Does M1 Finance Make Money, How Does Mint Make Money, How Does NerdWallet Make Money, How Does Acorns Make Money, How Does SoFi Make Money, How Does Stash Make Money, How Does Robinhood Make Money, How Does E-Trade Make Money, How Does Coinbase Make Money, How Does Affirm Make Money, Fintech Companies And Their Business Models.
List of FinTech Business Models




Braintree



















Read Next: Fintech Business Models, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Enterprise AI Business Model, Cloud Business Models.
Read Next: Affirm Business Model, Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:









thank you so much
you’re welcome 🙂