The FourWeekMBA Business Glossary guides you through key concepts to leverage to build a valuable company and a sustainable business model.
The continuous quest for problem-solving in the real world
Entrepreneurship is about solving problems by leveraging on markets’ feedback to develop products with high potential, which people want and desire.
Entrepreneurs then must understand some of the tools they can leverage to build valuable companies able to capture some of the value delivered through their products and services and build sustainable business models.

Read the full guide on What Is Entrepreneurship
Bootstrap your way to sustainable growth

Brand equity as a lasting asset
When business model innovation is achieved, and a sustainable business model is built, a company can also leverage its brand equity as an additional long-term advantage.

Read the full guide on Brand Equity
Business model innovation as a competitive advantage
When all the things above are met, business model innovation becomes a propeller that drives long-term advantage.

Read the full guide on Business Model Innovation
Business modeling as a toolbox
One of the conceptual tools that entrepreneurs can leverage is a business model or a framework that helps them identify the key building blocks that by time to time a company is built upon.
Business modeling is useful to build valuable companies but also to observe existing companies in several industries to understand what parts of those companies can be borrowed.
By assembling those parts, and mixing them together with tinkering and experimentation that is how entrepreneurs can build a sustainable advantage.

Read the full guide on What Is a Business Model
Business design rather than business planning
In the times in which capital is easily available, companies put up hundreds of pages of business plans just to discover the next day how useless they were.
While in the past, using business planning made more sense. In the current times also, companies with substantial capital injections need fast validation from the market to build something sustainable.
Thus, where in the past, massive capital injections would be used as moats, capital without a sustainable business model won’t last long (see the most recent and exemplary WeWork case, but also at the rise of the dot-com bubble the Webvan case). Therefore, a company that wants to build something valuable needs to master business model design.
Business model design is not about sketch on a piece of paper, but that is about experimentation.

Read the full guide on Business Design
Business experimentation rather than business theory
Business experimentation is the key ingredient also when a company has massive capital injections because that strikes a balance and feedback loop which keeps companies grounded.
In short, a company that just uses capital to grow without testing whether its growth is sustainable in the marketplace will need a reality check sooner or later.
For that matter, a company built on the ground up with a continuous loop with the marketplace can grow organically and exponentially.

Read the full guide on What Is a Business Experimentation
Continuous iteration and market feedback loop
Therefore, the key to building a sustainable business model is about having a continuous feedback loop between vision (where you want to be in a decade from now), key customers (representing your ideal market at any given time), and offered value proposition.

Read the full guide on How to design a create model
Customer is the key investor
When your key customers love your product so much to make it grow organically and exponentially, that is when you hit the home run! What venture capitalists like to call Product-Market Fit.

Read the full guide on Product-Market Fit
Customer obsession as North Star

Design thinking and customer-centrism

Revenue modeling as a validation tool
For that matter, revenue modeling is very important in building a sustainable business model. Revenue modeling is about building revenue streams which are in line with the long-term vision of the brand.

Read the full guide on Revenue Streams

Beyond core functions and into psycho-logic
Mastering a core value proposition is a key step and the glue which keeps the whole business model together. Value can be seen from several perspectives, and it’s not just about functionality. In many cases, that is about psychology, what Rory Sutherland calls psycho-logic.

Key Highlights
- FourWeekMBA Business Glossary:
- A guide to understanding key concepts for building valuable companies and sustainable business models.
- Entrepreneurship and Problem-Solving:
- Entrepreneurship involves solving real-world problems by creating products that people want and need.
- Entrepreneurs use methodologies, systems, and experience to navigate challenges.
- Bootstrapping for Growth:
- Bootstrapping in business means using internal cash flows for growth.
- Mastering key customer segments is crucial for successful bootstrapping.
- Brand Equity for Long-Term Advantage:
- Brand equity is the premium customers pay for perceived value.
- Successful business model innovation can enhance brand equity.
- Business Model Innovation and Competitive Edge:
- Business model innovation propels long-term advantage.
- Crafting a compelling value proposition is key for innovation.
- Business Modeling as a Toolbox:
- Business models help identify key building blocks of a company.
- Models aid in understanding and borrowing from existing companies.
- Business Design for Sustainability:
- Business design is crucial for companies seeking sustainable success.
- Experimentation and risk validation are central to business design.
- Business Experimentation and Reality Checks:
- Business experimentation keeps companies grounded and sustainable.
- Organic and exponential growth is achievable through continuous testing.
- Continuous Iteration and Market Feedback:
- Building a sustainable model requires ongoing feedback loops.
- Define problems, customers, solutions, and monetization strategies.
- Customer-Centric Approach and Product-Market Fit:
- Customer love drives organic growth and success.
- Product-Market Fit signifies a good market and product alignment.
- Customer Obsession and Design Thinking:
- Customer obsession gathers insights from customer feedback.
- Design thinking balances people’s needs, technology, and business goals.
- Revenue Modeling for Validation:
- Revenue modeling aligns revenue streams with the brand’s vision.
- It’s a foundational element of a business model, influencing value delivery.
- Understanding Psycho-Logic and Value Propositions:
- Value propositions extend beyond functionality to psychology.
- Value can be generated through demand generation and customer identification.
Read the full guide on Value Proposition Design
Related Linked Resources:
- What Is Business Model Innovation
- What Is a Business Model
- What Is A Heuristic
- What Is Bounded Rationality
- What Is Business Development
- What Is Business Strategy
- What is Blitzscaling
- What Is a Value Proposition
- What Is a Lean Startup Canvas
- What Is Market Segmentation
- What Is a Marketing Strategy
- What is Growth Hacking
What is Entrepreneurship?

What is a Business Model?

What is a Digital Business Model?
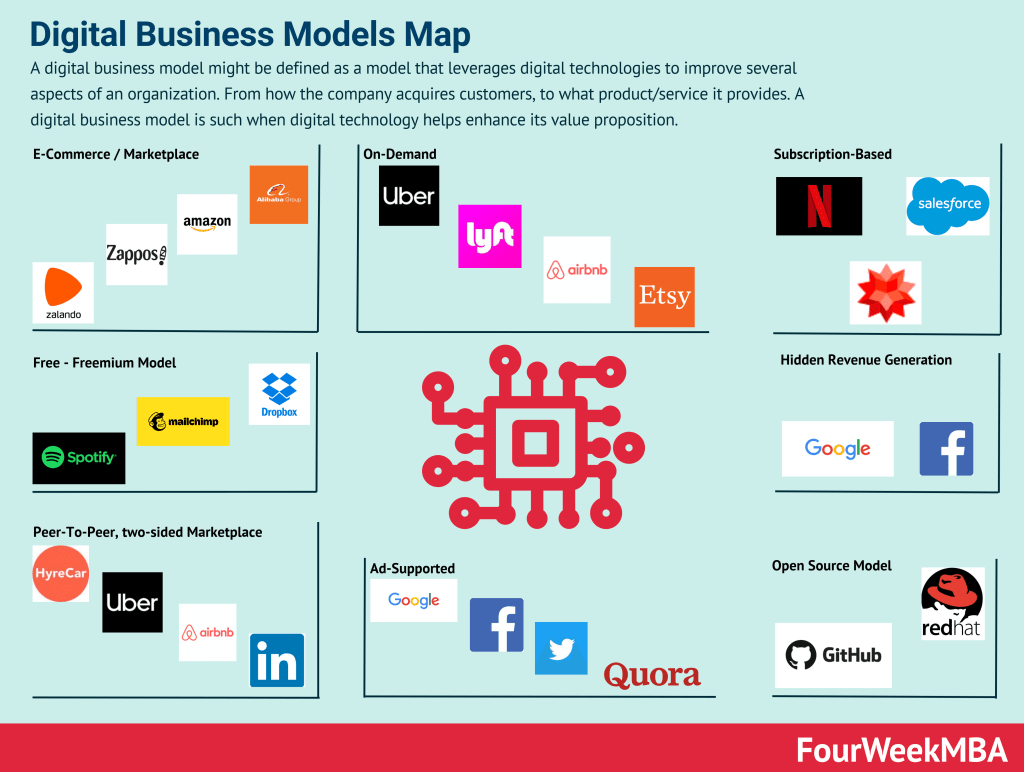
What is a Tech Business Model?

What is Business Analysis?

What is Agile Business Analysis?

What is a Competitor Analysis?

What is Design Thinking?

What is Business Model Innovation?

What is a Lean Startup?

What is an MVP?

What is Continuous Innovation?

What Is The Jobs-To-Be-Done Framework?

What is Growth Hacking?

FourWeekMBA Business Toolbox











Asymmetric Betting














