The Cost Structure building block of the Business Model Canvas details the monetary cost of operating as a business. Cost structure represents all the costs a business will incur under a specific business model, especially those costs to maintain the key resources that make up the core business model.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cost Structure | – Cost Structure is one of the nine building blocks in the Business Model Canvas, a strategic management tool that helps organizations describe, design, and analyze their business model. It outlines the types of costs a business incurs while operating. |
| Importance | – Understanding cost structure is crucial because it directly impacts a company’s profitability, pricing strategy, and overall financial health. An efficient cost structure can give a business a competitive advantage. |
| Categories | – Cost Structure is typically divided into two main categories: Fixed Costs and Variable Costs. – Fixed Costs remain constant regardless of production or sales volume (e.g., rent, salaries). – Variable Costs change in direct proportion to production or sales (e.g., materials, labor). |
| Key Considerations | – Businesses need to carefully manage their cost structure by optimizing their cost-to-value ratio. – Economies of scale can help reduce per-unit costs as production volume increases. – Innovations and new technologies can impact cost structures, making them more efficient. |
| Business Models | – Different business models have distinct cost structures. For example, a subscription-based model may have high initial customer acquisition costs but lower ongoing service costs. In contrast, a retail model may have significant inventory costs. |
| Cost Reduction | – Businesses often seek ways to reduce costs through process optimization, outsourcing, automation, and strategic sourcing. – Lean methodologies are commonly used to eliminate waste and reduce costs. |
| Revenue vs. Costs | – Achieving a balance between revenue generation and cost management is essential for profitability. A business must ensure that its revenue exceeds its total costs to generate a profit. |
| Cost Allocation | – Allocating costs accurately to specific products or services is vital for pricing decisions and identifying profitable offerings. It helps businesses understand which products or services contribute positively to the bottom line. |
| Scenario Analysis | – Businesses should conduct scenario analysis to understand how changes in production volume, pricing, or cost structure affect their financial performance. It helps in making informed decisions and managing financial risks. |
| Conclusion | – Cost Structure in the Business Model Canvas is a fundamental component that defines the types of costs a business incurs. Understanding and optimizing cost structure is essential for achieving profitability and long-term sustainability. |
Understanding cost structure in the Business Model Canvas
This is an important building block in the BMC, with 90% of businesses failing in under three years because they underestimate the cost of creating the goods and services outlined in their value proposition.
Operational costs encompass expenditure related to employees, infrastructure, activities, and partnerships.
These costs are defined by three other BMC building blocks: value proposition, revenue streams, and long-term customer relationships.
To gain clarity on the exact cost structure, however, it is important businesses also detail key resources, activities, and partnerships.
These are a few of the questions a business must consider when creating its cost structure:
- What are the fundamental costs of the business model?
- Which key activities cost the most to perform? Which key resources cost the most to perform?
- How do the key activities drive costs?
- Are key activities matched to the value proposition?
- Do costs become variable or remain fixed by considering other structures?
Cost structure types
While minimizing cost is fundamental to good business, organizations nonetheless employ different cost structure strategies.
Some are on a dogged mission to reduce costs as much as possible, while others pride themselves on their luxury or bespoke product ranges. In truth, most organizations are somewhere in between.
Various strategies occupy opposite ends of a cost structure spectrum, with a cost-driven structure at one end and a value-driven structure at the other.
With all that said, let’s take a look at both types in more detail:
Value-driven structure
A strategy where there is a complete focus on customer value at the expense of cost. Value is created by customizing the product or service to individual preferences.
Hyatt Hotel repeat customers are on a first-name basis with hotel staff and are provided with a personalized room before they arrive.
Cost-driven structure
Which focuses on minimizing the cost of a product or service wherever possible.
Businesses focus on creating a lean cost structure through cheap pricing, automation, and the outsourcing of costly activities.
Walmart uses immense economies of scale to reduce costs to a point where other retailers cannot compete.
Most budget airlines reduce costs by increasing seat capacity, not offering meals, and limiting luggage size.
Cost structure attributes
A typical cost structure, regardless of strategy or type, has one or more of the following attributes:
Economies of scale
Where a company with a high output quota benefits from a lower cost per unit amount.
This occurs because large volume orders spread fixed costs more evenly than smaller orders.
Economies of scale are common in large organizations that make bulk purchases from a supplier.
Economies of scope
Here, costs are reduced when an organization expands its operational scope or invests in multiple markets.
To derive maximum benefit from economies of scope, each product should require similar marketing messages or utilize the same distribution channel.
Fixed costs
Or business expenses that remain constant irrespective of volume.
Fixed costs can be time-bound, such as a fortnightly employee salary or monthly rent for an office space.
Manufacturing companies are also subject to fixed costs such as equipment and facility rental.
Fixed costs do not remain fixed indefinitely and will change over time while remaining relatively stable.
Variable costs
These are costs that are heavily dependent on volume output and are influenced by supply and demand.
In a production scenario, variable costs may be associated with sourcing raw materials, utility bills, and employee labor.
Cost structure examples
In the final section, let’s take a look at a few cost structure examples from some notable companies.
Netflix

The cost structure of Netflix was significant enough in the company’s early days to impact cash flow and growth. Some of these costs include:
- The acquisition, production, delivery, and licensing of streaming content. These are likely to be the largest costs for the company today.
- Platform maintenance.
- Software development.
- Research and patents.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) for database, analytics, recommendation engines, and video transcoding, to name a few functions.
- Data centers to provide streaming content.
- Marketing, human resources, and related infrastructure.
Netflix has also benefitted from economies of scope and key activities that match its value proposition.
Nike
The cost structure of Nike is such that the company pockets a relatively small amount of profit from each item it sells. Costs associated with the sale of a pair of sneakers, for example, include:
- Retail markup – this is as high as 50% of the total purchase price in some cases.
- Sea freight and insurance.
- Free on Board (FOB) costs, which cover the cost of shipping from the factory.
- Selling, general, and administrative expenses.
- Customs duties and taxes.
In addition to these costs, Nike spends billions on advertising, marketing, sponsorships, brand presentation, and other promotional costs. In 2021, this amounted to $3.11 billion.
Tesla

Tesla’s cost structure is characterized by fixed manufacturing costs. For each vehicle that rolls off the production line, these include equipment (20%), body (12%), chassis (7%), drive system (15%), battery (35%), and other (11%).
In addition, Tesla has the following costs:
- Research and development – consisting of personnel costs related to engineering, research, prototyping, contract and professional services, and costs from amortized equipment.
- Selling, general and administrative expenses – personal and facilities related costs such as stores, sales, finances, human resources, information technology, and any fees related to legal or contract services and litigation settlements.
- Restructuring and others – including employee termination costs, disposal of tangible assets, facility sub-leasing losses, and impairment losses.
- Interest and taxes.
Airbnb

Airbnb has a relatively simple cost structure when compared to some of its competitors in the hotel industry.
This is because the company does not own the accommodation listed on its website and as a result, avoids the many costs associated with hospitality staff and hotel upkeep.
The company’s cost structure consists of the following:
- Cost of revenue – which includes online payment processing fees that are paid to Visa and Mastercard. Cost of revenue also encompasses insurance. In the rare event that a guest, host, or cleaner is injured or has their personal property damaged or stolen, Airbnb is responsible for paying out insurance claims.
- Sales and marketing – such as customer acquisition, customer retention, discounts, promotions, referral fees, and refunds.
- Research and development – there are also costs associated with ensuring the Airbnb platform is functional, on-trend, intuitive, and streamlined. Other research and development costs include engineering and product development.
- General and administration – this includes costs related to administration and employees such as HR and finance, legal fees, executives, general managers, and professional services such as freelance photography.
Key takeaways
- The Cost Structure building block of the Business Model Canvas details the monetary cost of operating as a business. This block is important to get right since many businesses fail due to misunderstanding or underestimating their costs.
- Cost-structures may be value-driven or cost-driven. As the name suggests, value-driven structures focus on delivering customer value at the expense of minimizing cost. In a cost-driven structure, the opposite is true.
- Regardless of type, most cost-structure have one or more of the following attributes: economies of scale, economies of scope, fixed costs, and variable costs.
Key Highlights
- Cost Structure Defined: The cost structure is a fundamental building block in the Business Model Canvas (BMC), which outlines the monetary costs associated with operating a business. It encompasses all expenses necessary to maintain the key resources that form the core of the business model.
- Importance of Cost Structure: Many businesses fail within the first three years because they often underestimate the costs involved in delivering the goods and services outlined in their value proposition. Understanding and managing cost structure is crucial for sustainability.
- Operational Costs: Operational costs cover expenditures related to employees, infrastructure, activities, and partnerships. These costs are influenced by other BMC building blocks, including the value proposition, revenue streams, and long-term customer relationships.
- Detailed Understanding: To gain a clear understanding of cost structure, businesses should also consider and detail key resources, activities, and partnerships, as these factors directly impact costs.
- Key Questions: When creating a cost structure, businesses should address important questions such as fundamental costs, costliest key activities and resources, the relationship between key activities and costs, alignment with the value proposition, and the potential for variable or fixed costs.
- Cost Structure Types: Different organizations adopt varying cost structure strategies, ranging from a strong focus on reducing costs to a focus on delivering high customer value. Two main types are highlighted: value-driven and cost-driven structures.
- Value-Driven Structure: In a value-driven cost structure, the primary emphasis is on delivering exceptional customer value, often at the expense of higher costs. Customization and personalized services are common features. For example, Hyatt Hotel provides personalized services to repeat customers.
- Cost-Driven Structure: A cost-driven cost structure prioritizes minimizing costs wherever possible. Companies focus on creating a lean cost structure through strategies like cost-effective pricing, automation, and outsourcing. Walmart’s use of economies of scale and budget airlines’ cost-cutting measures are examples.
- Cost Structure Attributes: Regardless of the type of cost structure, several attributes can be found:
- Economies of Scale: Larger companies with high output can benefit from lower costs per unit due to the spreading of fixed costs, common in bulk purchasing.
- Economies of Scope: Cost reduction occurs as an organization expands its operations or enters multiple markets, particularly when products share marketing or distribution channels.
- Fixed Costs: Expenses that remain constant regardless of output volume, such as salaries or rent.
- Variable Costs: Costs heavily dependent on output volume and influenced by supply and demand, such as raw materials and utility bills.
- Cost Structure Examples: The article provides cost structure examples from notable companies:
- Netflix: Costs associated with content acquisition, production, delivery, platform maintenance, software development, research, and infrastructure.
- Nike: Costs related to retail markup, shipping, customs duties, advertising, marketing, and promotional expenses.
- Tesla: Fixed manufacturing costs for equipment, body, chassis, drive system, battery, and other components, along with research and development, administrative expenses, and interest and taxes.
- Airbnb: Costs of revenue (payment processing fees and insurance), sales and marketing, research and development, and general administration.
- Sustainability and Profitability: Understanding and managing cost structures are crucial for a business’s sustainability and profitability. Companies must strike a balance between minimizing costs and delivering value to customers.
- Adaptability: Cost structures may evolve over time in response to changing market conditions, technology advancements, and shifts in customer preferences. Adaptation is essential for long-term success.
What are the 2 cost structure types?
The two main types of cost structures are:
What are the attributes of a cost structure?
The main attributes of a cost structure are:
What's Netflix cost structure?
Netflix’s cost structure comprises:
- The acquisition, production, delivery, and licensing of streaming content.
- Platform maintenance.
- Software development.
- Research and patents.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Data centers to provide streaming content.
- Marketing, human resources, and related infrastructure.
Alternatives to the Business Model Canvas
FourWeekMBA Squared Triangle Business Model
This framework has been thought for any type of business model, be it digital or not. It’s a framework to start mind mapping the key components of your business or how it might look as it grows. Here, as usual, what matters is not the framework itself (let’s prevent to fall trap of the Maslow’s Hammer), what matters is to have a framework that enables you to hold the key components of your business in your mind, and execute fast to prevent running the business on too many untested assumptions, especially about what customers really want. Any framework that helps us test fast, it’s welcomed in our business strategy.

FourWeekMBA VTDF Framework For Tech Business Models
This framework is well suited for all these cases where technology plays a key role in enhancing the value proposition for the users and customers. In short, when the company you’re building, analyzing, or looking at is a tech or platform business model, the template below is perfect for the job.


Download The VTDF Framework Template Here
FourWeekMBA VBDE Framework For Blockchain Business Models
This framework is well suited to analyze and understand blockchain-based business models. Here, the underlying blockchain protocol, and the token economics behind it play a key role in aligning incentives and also in creating disincentives for the community of developers, individual contributors, entrepreneurs, and investors that enable the whole business model. The blockchain-based model is similar to a platform-based business model, but with an important twist, decentralization should be the key element enabling both decision-making and how incentives are distributed across the network.

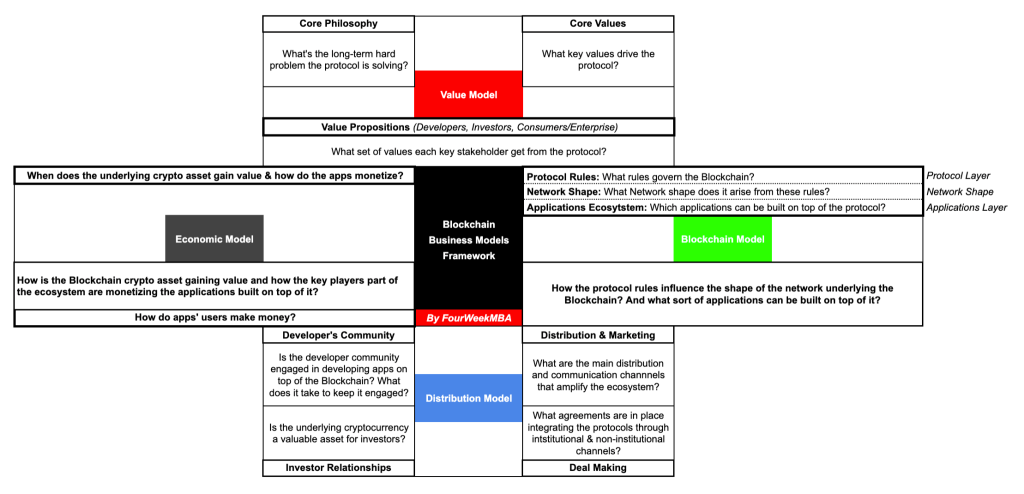
Download The VBDE Framework Template Here
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
Connected Business Concepts























